https://yogyui.tistory.com/entry/Raspberry-Pi-Docker-%EC%84%A4%EC%B9%98%ED%95%98%EA%B8%B0
Raspberry Pi - Docker 설치하기
Install Docker on Raspberry Pi (Raspbian OS) 컨테이너(Container) 솔루션 중 가장 널리 사용되는 Docker는 Raspbian에 번들로 포함되어 있지 않아 사용자가 수동으로 설치해줘야 한다 DevOps 플랫폼 중 하나인 JFrog
yogyui.tistory.com
https://dev.to/elalemanyo/how-to-install-docker-and-docker-compose-on-raspberry-pi-1mo
How To Install Docker and Docker-Compose On Raspberry Pi
RaspberryPi ARMed with Docker and Docker-Compose
dev.to
How To Install Docker and Docker-Compose On Raspberry Pi
Prerequisites
- Raspberry Pi with a running Raspbian OS
- SSH connection enabled
To do this you can check Raspberry Pi Setup.
1. Update and Upgrade
First of all make sure that the system runs the latest version of the software.
Run the command:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
2. Install Docker
Now is time to install Docker! Fortunately, Docker provides a handy install script for that, just run:
curl -fsSL test.docker.com -o get-docker.sh && sh get-docker.sh
3. Add a Non-Root User to the Docker Group
By default, only users who have administrative privileges (root users) can run containers. If you are not logged in as the root, one option is to use the sudo prefix.
However, you could also add your non-root user to the Docker group which will allow it to execute docker commands.
The syntax for adding users to the Docker group is:
sudo usermod -aG docker [user_name]
To add the permissions to the current user run:
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
Check it running:
groups ${USER}
Reboot the Raspberry Pi to let the changes take effect.
4. Install Docker-Compose
Docker-Compose usually gets installed using pip3. For that, we need to have python3 and pip3 installed. If you don't have it installed, you can run the following commands:
sudo apt-get install libffi-dev libssl-dev
sudo apt install python3-dev
sudo apt-get install -y python3 python3-pip
Once python3 and pip3 are installed, we can install Docker-Compose using the following command:
sudo pip3 install docker-compose
5. Enable the Docker system service to start your containers on boot
This is a very nice and important addition. With the following command you can configure your Raspberry Pi to automatically run the Docker system service, whenever it boots up.
sudo systemctl enable docker
With this in place, containers with a restart policy set to always or unless-stopped will be re-started automatically after a reboot.
6. Run Hello World Container
The best way to test whether Docker has been set up correctly is to run the Hello World container.
To do so, type in the following command:
docker run hello-world
Once it goes through all the steps, the output should inform you that your installation appears to be working correctly.
7. A sample Docker Compose file
This section shows a quick sample of a Docker-Compose file, which starts three containers that once started will automatically come up, if the Raspberry Pi get fully power cycled. To learn more about the sample project, visit Docker Speed Test project on GitHub.
version: '3'
services:
# Tests the current internet connection speed
# once per hour and writes the results into an
# InfluxDB instance
speedtest:
image: robinmanuelthiel/speedtest:0.1.1
restart: always
depends_on:
- influxdb
environment:
- LOOP=true
- LOOP_DELAY=3600 # Once per hour
- DB_SAVE=true
- DB_HOST=http://influxdb:8086
- DB_NAME=speedtest
- DB_USERNAME=admin
- DB_PASSWORD=<MY_PASSWORD>
# Creates an InfluxDB instance to store the
# speed test results
influxdb:
image: influxdb
restart: always
volumes:
- influxdb:/var/lib/influxdb
ports:
- "8083:8083"
- "8086:8086"
environment:
- INFLUXDB_ADMIN_USER=admin
- INFLUXDB_ADMIN_PASSWORD=<MY_PASSWORD>
- INFLUXDB_DB=speedtest
# Displays the results in a Grafana dashborad
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
restart: always
depends_on:
- influxdb
ports:
- 3000:3000
volumes:
- grafana:/var/lib/grafana
volumes:
grafana:
influxdb:
To start the containers using Docker-Compose, run the following command:
docker-compose -f docker-compose.yaml up -d
Find Raspberry Pi Docker Images
Raspberry Pi is based on ARM architecture. Hence, not all Docker images will work on your Raspberry Pi.
Remember that when searching for images to pull from Docker Hub. Apply the Architectures filter to search for supported apps.
How to Upgrade Docker on Raspberry Pi?
Upgrade Docker using the package manager with the command:
sudo apt-get upgrade
How to Uninstall Docker on Raspberry Pi?
You can simply remove docker using the package manager:
sudo apt-get purge docker-ce
Note: Depending on the version of software, you may need to use an additional command to completely remove Docker:
sudo apt-get purge docker-ce-cli
To delete leftover images, containers, volumes and other related data, run the following command:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
Edited configuration files must be deleted manually.
References
Setup your Raspberry Pi for Docker and Docker-Compose
Personally, I like to use Docker containers on my Raspberry Pis as they come with a great layer of abstraction and portability. Here is how to get your Raspberry Pi ready for Docker and Docker-Compose. 1. Setup your Raspberry Pi with Raspbian, Wifi and SSH
pumpingco.de
https://www.robotstory.co.kr/raspberry/?vid=32
라즈베리파이OS에 도커(Docker) 설치하기
1. 도커란?도커라고 들어보셨나요? 도커는 컨테이너 기반 오픈소스 가상화 플랫폼입니다.컨테이너란 격리된 공간에서 프로세스가 실행되도록 하는 기술입니다.버추얼머신(VM)이라고 들어보셨을
www.robotstory.co.kr
1. 도커란?
도커라고 들어보셨나요?
도커는 컨테이너 기반 오픈소스 가상화 플랫폼입니다.
컨테이너란 격리된 공간에서 프로세스가 실행되도록 하는 기술입니다.
버추얼머신(VM)이라고 들어보셨을겁니다. 버추얼머신은 격리된 공간에서 OS가 실행되도록 하는 기술입니다. 윈도우에 격리된 리눅스를 설치한 것이라 보면 됩니다. 쉽게말해서 컴퓨터 안에 가상의 컴퓨터가 있는겁니다.
버추얼머신은 이미 설치되어 있는 OS위에 새로운 OS를 실행시키기때문에 조금 무겁습니다.
그에 비해 도커는 기존 OS 위에 격리된 프로세스 공간을 만들어 실행시키때문에 가볍고 빠르게 동작합니다.
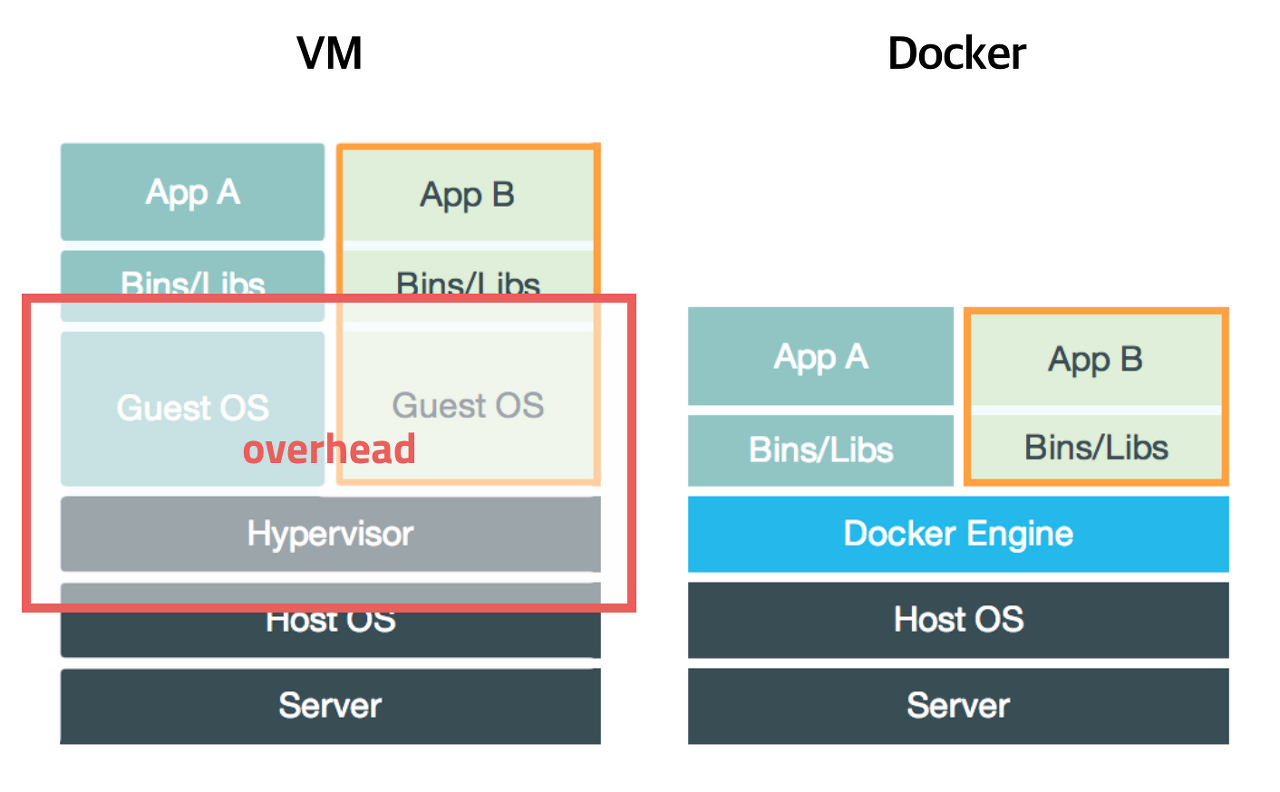
그렇다면 왜 도커를 사용할까요? 기존 OS위에서 프로세스를 실행시키면 되지않을까요?
이는 프로그램마다 운영환경이 다르기때문입니다.
예를 들어 A라는 프로그램은 파이썬3.8을 기반으로 작동하는데 OS에는 파이썬 3.5가 설치되어있다면 파이썬3.8을 추가적으로 설치해야합니다. '그럼 그냥 파이썬 3.8을 설치하면 되지'라고 생각하는 분도 있을겁니다. 하지만 프로그램은 무수히 많고 프로그램을 설치할때마다 환경을 따로 설정하는 것은 여간 번거로운 일이 아닙니다.
도커를 사용한다면 격리된 가상의 공간에 배포자가 작성한 운영환경에 필요한 라이브러리를 설치하여 프로세스를 실행시키게 됩니다. 즉 따로 프로그램에 맞춰 환경설정을 할 필요가 없다는 뜻입니다.
2. 도커 설치
우선 라즈베리파이에 원격로그인합니다.
윈도우를 기준으로 명령프롬프트를 이용하도록 하겠습니다.
win키 + R을 눌러 실행창을 열고 cmd를 입력하여 명령프롬프트를 엽니다.
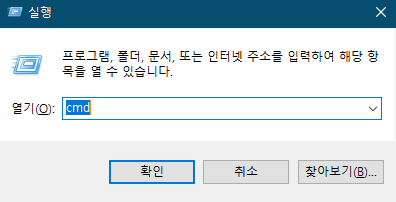
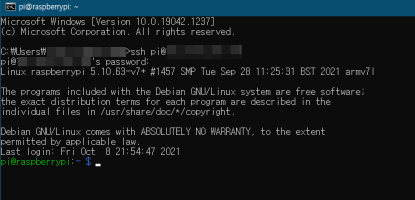
다음 명령어를 입력하여 라즈베리파이에 로그인합니다.
비밀번호는 저번 글에서 설정했습니다.
| > ssh pi@ip주소 |
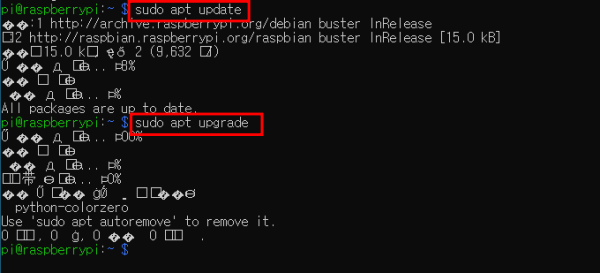
다음 명령어를 입력하여 라즈베리파이를 최신상태로 업데이트 합니다.
| > sudo apt update ... > sudo apt upgrade |
다음 명령어를 입력하면 도커가 설치됩니다.
| > sudo curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com/ | sudo sh |

다음 명령어를 입력하여 도커가 설치되었는지 확인합니다.
| > docker ps |
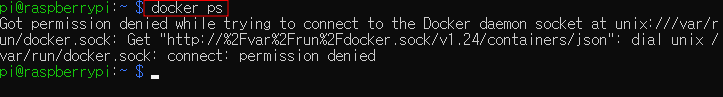
권한이 없다고 나옵니다. 아래 명령어를 입력하여 도커권한을 부여합니다.
| > sudo usermod -aG docker pi |
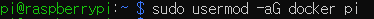
재부팅하면 권한이 부여되어 있습니다.
3. 포테이너(Portainer) 설치
포테이너는 도커를 웹으로 관리하는 도구입니다. 포테이너를 도커에 설치하겠습니다.
우선 포테이너 데이터를 저장할 볼륨(공간)을 만듭니다.
| > docker volume create portainer_data |
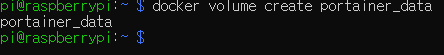
아래 명령어를 입력하여 포테이너 컨테이너를 만듭니다.
| > docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --name portainer --restart always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer-ce |
-d : 백그라운드모드(detached mode) 실행
-p 9000:9000 : 호스트 포트를 컨테이너 포트에 연결 (호스트:컨테이너)
--name portainer : 컨테이너 이름
--restart aloways : 도커 실행시 컨테이너 실행 여부
-v 호스트:컨테이너 : 호스트 볼륨을 컨테이너 볼륨에 연결
portainer/portainer-ce : 이미지 이름

http://라즈베리파이 ip주소:9000 로 이동합니다.
로그인 계정을 만듭니다.
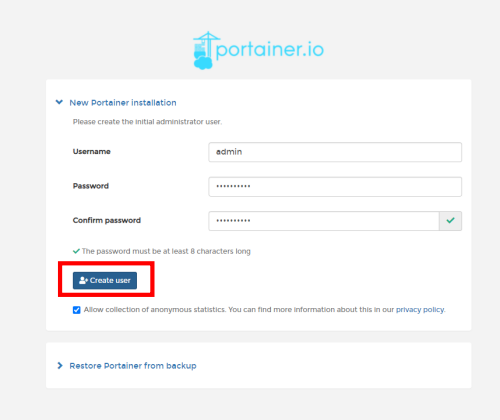
환경설정을 합니다.(로컬환경)

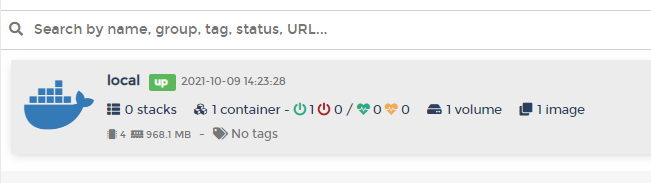
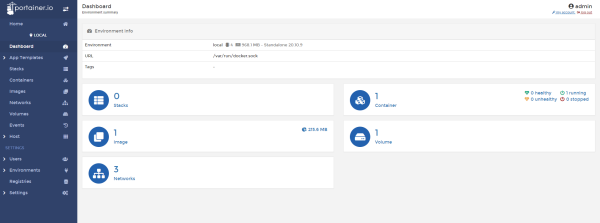
도커 상태를 확인할 수 있습니다. 컨테이너가 하나 생성되어있습니다. 포테이너 입니다.
'라즈베리파이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Finding Raspberry Pi IP address using nmap (0) | 2023.08.20 |
|---|---|
| [Raspberry Pi]Raspberry Pi 4에 Windows 11을 설치하는 방법 (0) | 2023.07.21 |
| Raspberry Pi 4에 Windows 11을 설치하는 방법 (0) | 2023.07.13 |
| Installation of Raspberry PiCar-A Program with OpenCV FPV Function (0) | 2022.07.21 |
| 2016. 04. 07 OCR on Rasberry Pi (Translation, 한글번역) (0) | 2022.05.24 |



댓글