[Flutter] mp3 사운드 파일 재생 하기 (매우 간단하게..)
우리의 시간은 소중하니까 플러터에서 소리 파일을 재생하려고 찾아보니 audioplayers 패키지가 나온다. LIKES 와 POPULARITY 를 확인 보니 그냥 이거 사용하라는 말이다. 그런데 문제가 생겼다. Getting St
xcevor.tistory.com
플러터에서 소리 파일을 재생하려고 찾아보니 audioplayers 패키지가 나온다.
LIKES 와 POPULARITY 를 확인 보니 그냥 이거 사용하라는 말이다.
그런데 문제가 생겼다.
Getting Started tutorial 을 따라 해도 안 되는.. 이런..
왜 그런지는 모르겠는데 일단 되는 방법을 찾아서 포스팅해둔다.
현시점 (22년 11월) 에서 되는 것이기에 패키지가 업데이트되거나 변경되면 방법이 달라질 수 있다. (1년 전.. 몇 달 전 유튜브 정보조차 안 맞음.)
따라서 플러터 기본 앱에 코드를 추가하여 빠르게 작동 확인을 해보고 다음 응용 단계를 밟자는 것이 이 포스팅의 의도이다. 뻘짓 싫어 ㅠㅠ
기본 카운터 앱에 버튼 하나 추가시켜 플레이 해보기
우리의 시간은 소중하니까.
패키지 설치 및 설정 하기
https://pub.dev/packages/audioplayers
audioplayers | Flutter Package
A Flutter plugin to play multiple audio files simultaneously
pub.dev
현재 포스팅하는 시점의 최신 버전은 audioplayers: ^1.1.1 이다.
프로젝트를 생성하면 플러터 기본 카운터 앱이 작성된다.
이제 assets 폴더를 만들고 로컬 테스트에 쓸 mp3 파일을 넣어 준다.
(웹에 있는 mp3 파일을 재생한다면 안 해도 됨)
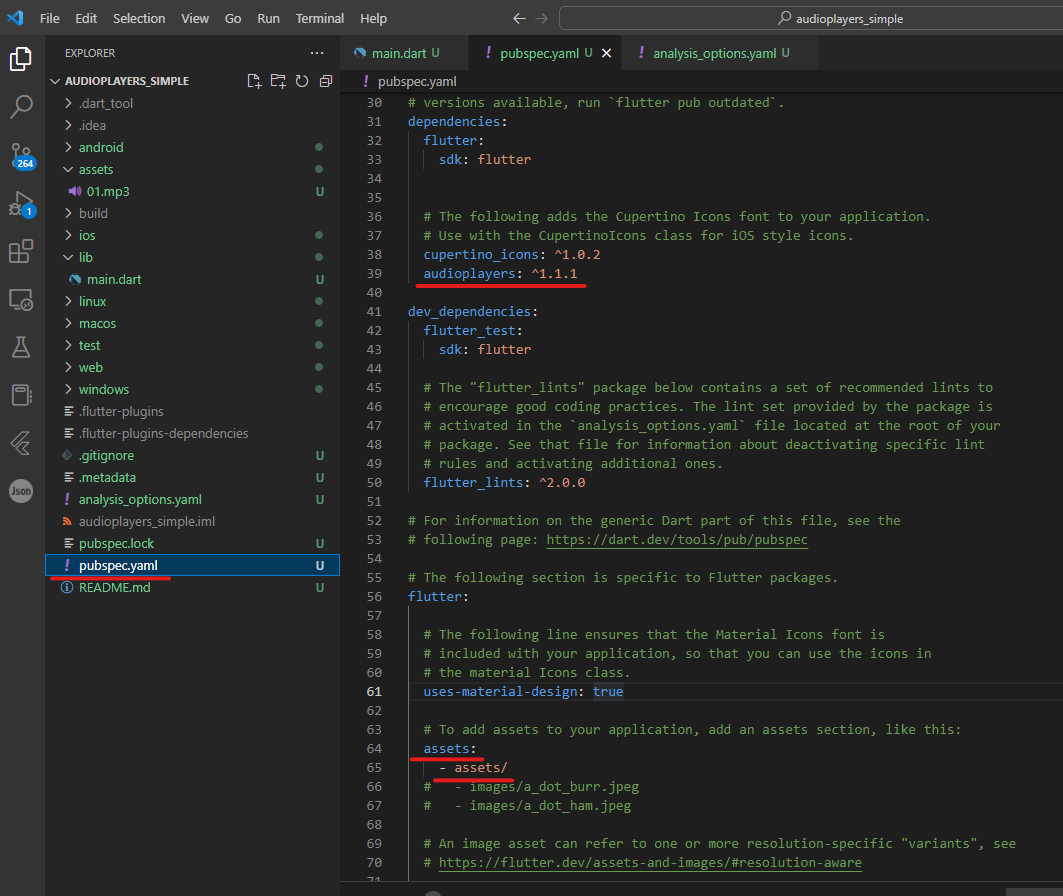
그리고, pubspec.yaml 파일에 들어가
audioplayers: ^1.1.1
패키지를 를 추가시켜 주고
assets:
- assets/
에셋을 설정해 준후 저장한다.
코드 추가
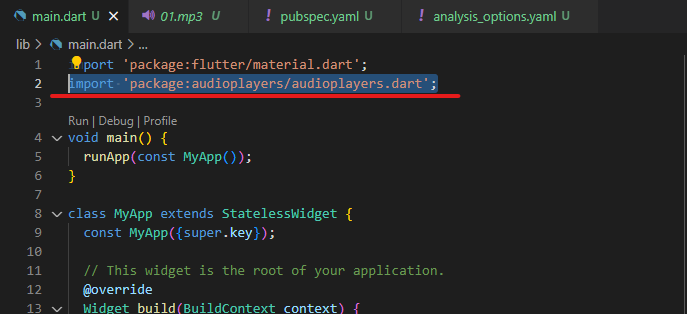
import 'package:audioplayers/audioplayers.dart';
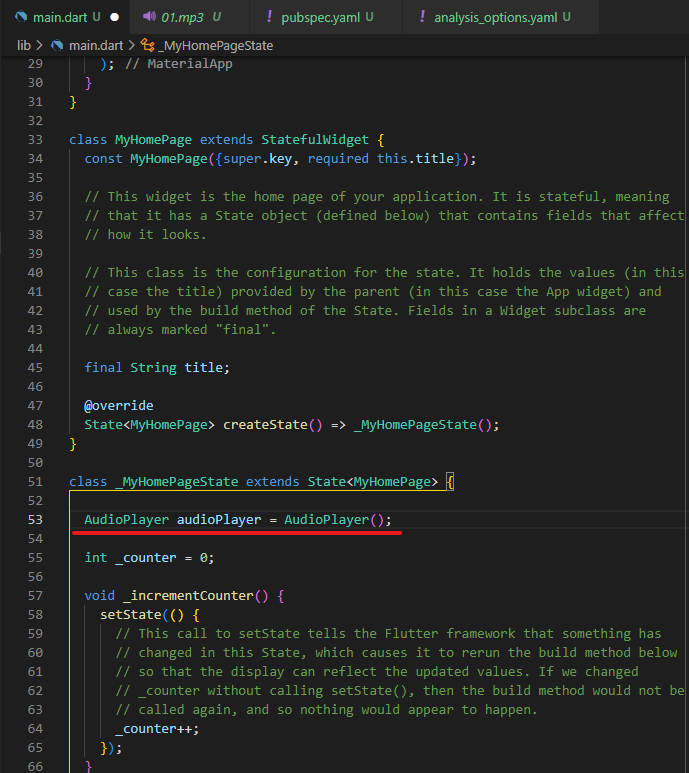
AudioPlayer audioPlayer = AudioPlayer();
IconButton 으로 사이즈던 색상이던 아무런 꾸미기 없이 required 만 만족시켜 누를 수 있는 기능 구성만 한다.
내부 저장소 assets 에 있는 wav 파일 재생
|
|
IconButton( |
|
|
onPressed: (() async { |
|
|
await audioPlayer.play(AssetSource('xxx.wav')); |
|
|
}), |
|
|
icon: Icon(Icons.play_arrow), |
|
|
), |
AssetSource() 안에는 상대 경로 "assets/" 을 붙이지 않아도 된다.
(assets/assets/xxx.wav 메시지를 냄. 기본 적용되어있음. )
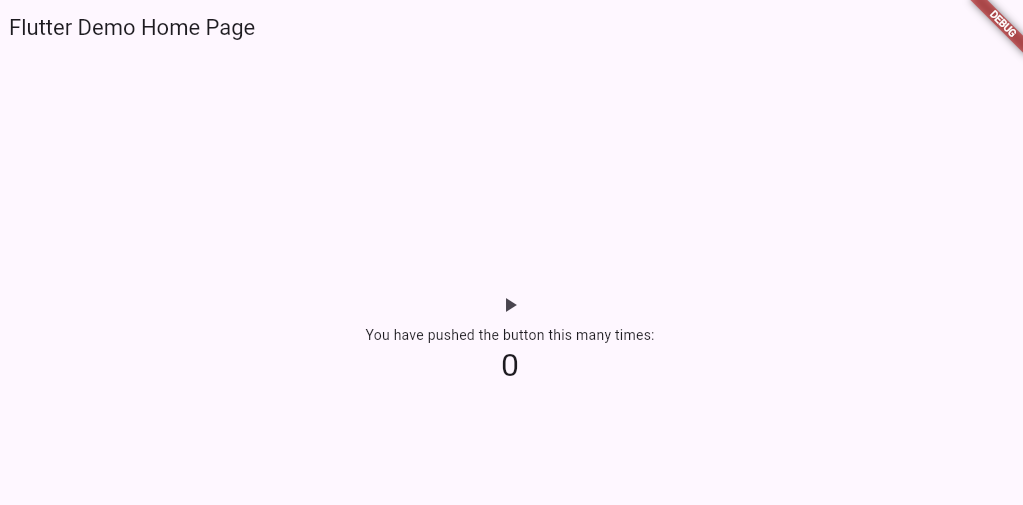
작동 모습
기존 카운트 앱 중간에 플레이 버튼이 하나 생성되었고 이것을 누르면 음악이 재생된다. 혹시 소리가 안난다면 음량을 올려본다.
pubspec.yaml
name: audioplay
description: "A new Flutter project."
# The following line prevents the package from being accidentally published to
# pub.dev using `flutter pub publish`. This is preferred for private packages.
publish_to: 'none' # Remove this line if you wish to publish to pub.dev
# The following defines the version and build number for your application.
# A version number is three numbers separated by dots, like 1.2.43
# followed by an optional build number separated by a +.
# Both the version and the builder number may be overridden in flutter
# build by specifying --build-name and --build-number, respectively.
# In Android, build-name is used as versionName while build-number used as versionCode.
# Read more about Android versioning at https://developer.android.com/studio/publish/versioning
# In iOS, build-name is used as CFBundleShortVersionString while build-number is used as CFBundleVersion.
# Read more about iOS versioning at
# https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/General/Reference/InfoPlistKeyReference/Articles/CoreFoundationKeys.html
# In Windows, build-name is used as the major, minor, and patch parts
# of the product and file versions while build-number is used as the build suffix.
version: 1.0.0+1
environment:
sdk: ^3.5.4
# Dependencies specify other packages that your package needs in order to work.
# To automatically upgrade your package dependencies to the latest versions
# consider running `flutter pub upgrade --major-versions`. Alternatively,
# dependencies can be manually updated by changing the version numbers below to
# the latest version available on pub.dev. To see which dependencies have newer
# versions available, run `flutter pub outdated`.
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
audioplayers: ^6.0.0
# The following adds the Cupertino Icons font to your application.
# Use with the CupertinoIcons class for iOS style icons.
cupertino_icons: ^1.0.8
dev_dependencies:
flutter_test:
sdk: flutter
# The "flutter_lints" package below contains a set of recommended lints to
# encourage good coding practices. The lint set provided by the package is
# activated in the `analysis_options.yaml` file located at the root of your
# package. See that file for information about deactivating specific lint
# rules and activating additional ones.
flutter_lints: ^4.0.0
# For information on the generic Dart part of this file, see the
# following page: https://dart.dev/tools/pub/pubspec
# The following section is specific to Flutter packages.
flutter:
# The following line ensures that the Material Icons font is
# included with your application, so that you can use the icons in
# the material Icons class.
uses-material-design: true
# To add assets to your application, add an assets section, like this:
# assets:
# - images/a_dot_burr.jpeg
# - images/a_dot_ham.jpeg
assets:
- assets/sample-9s.wav
# An image asset can refer to one or more resolution-specific "variants", see
# https://flutter.dev/to/resolution-aware-images
# For details regarding adding assets from package dependencies, see
# https://flutter.dev/to/asset-from-package
# To add custom fonts to your application, add a fonts section here,
# in this "flutter" section. Each entry in this list should have a
# "family" key with the font family name, and a "fonts" key with a
# list giving the asset and other descriptors for the font. For
# example:
# fonts:
# - family: Schyler
# fonts:
# - asset: fonts/Schyler-Regular.ttf
# - asset: fonts/Schyler-Italic.ttf
# style: italic
# - family: Trajan Pro
# fonts:
# - asset: fonts/TrajanPro.ttf
# - asset: fonts/TrajanPro_Bold.ttf
# weight: 700
#
# For details regarding fonts from package dependencies,
# see https://flutter.dev/to/font-from-package
main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:audioplayers/audioplayers.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
//
// Try running your application with "flutter run". You'll see the
// application has a blue toolbar. Then, without quitting the app, try
// changing the primarySwatch below to Colors.green and then invoke
// "hot reload" (press "r" in the console where you ran "flutter run",
// or simply save your changes to "hot reload" in a Flutter IDE).
// Notice that the counter didn't reset back to zero; the application
// is not restarted.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: const MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
AudioPlayer audioPlayer = AudioPlayer();
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
IconButton(
onPressed: (() async {
await audioPlayer.play(AssetSource('sample-9s.wav'));
}),
icon: const Icon(Icons.play_arrow),
),
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineLarge,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
댓글