반응형
https://github.com/makeyourownneuralnetwork/gan
GitHub - makeyourownneuralnetwork/gan: python notebooks accompanying the book Make Your Own GAN
python notebooks accompanying the book Make Your Own GAN - GitHub - makeyourownneuralnetwork/gan: python notebooks accompanying the book Make Your Own GAN
github.com
View Code ====>
Simple 1010 Pattern
Make Your First GAN With PyTorch, 2020
In [0]:
# import libraries
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import pandas
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import numpy
Data Functions
In [0]:
# function to generate real data
def generate_real():
real_data = torch.FloatTensor(
[random.uniform(0.8, 1.0),
random.uniform(0.0, 0.2),
random.uniform(0.8, 1.0),
random.uniform(0.0, 0.2)])
return real_data
In [0]:
# function to generate uniform random data
def generate_random(size):
random_data = torch.rand(size)
return random_data
Discriminator Network
In [0]:
# discriminator class
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
# initialise parent pytorch class
super().__init__()
# define neural network layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(4, 3),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(3, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
# create loss function
self.loss_function = nn.MSELoss()
# create optimiser, simple stochastic gradient descent
self.optimiser = torch.optim.SGD(self.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# counter and accumulator for progress
self.counter = 0;
self.progress = []
pass
def forward(self, inputs):
# simply run model
return self.model(inputs)
def train(self, inputs, targets):
# calculate the output of the network
outputs = self.forward(inputs)
# calculate loss
loss = self.loss_function(outputs, targets)
# increase counter and accumulate error every 10
self.counter += 1;
if (self.counter % 10 == 0):
self.progress.append(loss.item())
pass
if (self.counter % 10000 == 0):
print("counter = ", self.counter)
pass
# zero gradients, perform a backward pass, update weights
self.optimiser.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimiser.step()
pass
def plot_progress(self):
df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])
df.plot(ylim=(0, 1.0), figsize=(16,8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5))
pass
pass
Test Discriminator
In [0]:
# test discriminator can separate real data from random noise
D = Discriminator()
for i in range(10000):
# real data
D.train(generate_real(), torch.FloatTensor([1.0]))
# fake data
D.train(generate_random(4), torch.FloatTensor([0.0]))
pass
counter = 10000
counter = 20000
In [0]:
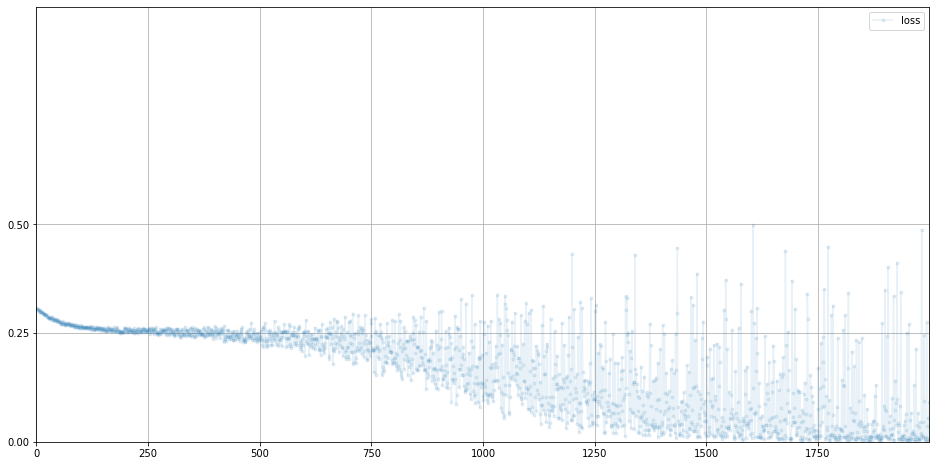
# plot discriminator loss
D.plot_progress()
In [0]:
# manually run discriminator to check it can tell real data from fake
print( D.forward( generate_real() ).item() )
print( D.forward( generate_random(4) ).item() )
0.8236010670661926
0.22374509274959564
Generator Network
In [0]:
# generator class
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
# initialise parent pytorch class
super().__init__()
# define neural network layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1, 3),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(3, 4),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
# create optimiser, simple stochastic gradient descent
self.optimiser = torch.optim.SGD(self.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# counter and accumulator for progress
self.counter = 0;
self.progress = []
pass
def forward(self, inputs):
# simply run model
return self.model(inputs)
def train(self, D, inputs, targets):
# calculate the output of the network
g_output = self.forward(inputs)
# pass onto Discriminator
d_output = D.forward(g_output)
# calculate error
loss = D.loss_function(d_output, targets)
# increase counter and accumulate error every 10
self.counter += 1;
if (self.counter % 10 == 0):
self.progress.append(loss.item())
pass
# zero gradients, perform a backward pass, update weights
self.optimiser.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimiser.step()
pass
def plot_progress(self):
df = pandas.DataFrame(self.progress, columns=['loss'])
df.plot(ylim=(0, 1.0), figsize=(16,8), alpha=0.1, marker='.', grid=True, yticks=(0, 0.25, 0.5))
pass
pass
Test Generator Output
In [0]:
# check the generator output is of the right type and shape
G = Generator()
G.forward(torch.FloatTensor([0.5]))
Out[0]:
tensor([0.4369, 0.5104, 0.3246, 0.5549], grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward>)Train GAN
In [0]:
%%time
# create Discriminator and Generator
D = Discriminator()
G = Generator()
image_list = []
# train Discriminator and Generator
for i in range(10000):
# train discriminator on true
D.train(generate_real(), torch.FloatTensor([1.0]))
# train discriminator on false
# use detach() so gradients in G are not calculated
D.train(G.forward(torch.FloatTensor([0.5])).detach(), torch.FloatTensor([0.0]))
# train generator
G.train(D, torch.FloatTensor([0.5]), torch.FloatTensor([1.0]))
# add image to list every 1000
if (i % 1000 == 0):
image_list.append( G.forward(torch.FloatTensor([0.5])).detach().numpy() )
pass
counter = 10000
counter = 20000
CPU times: user 15 s, sys: 1.29 s, total: 16.3 s
Wall time: 16.3 s
In [0]:
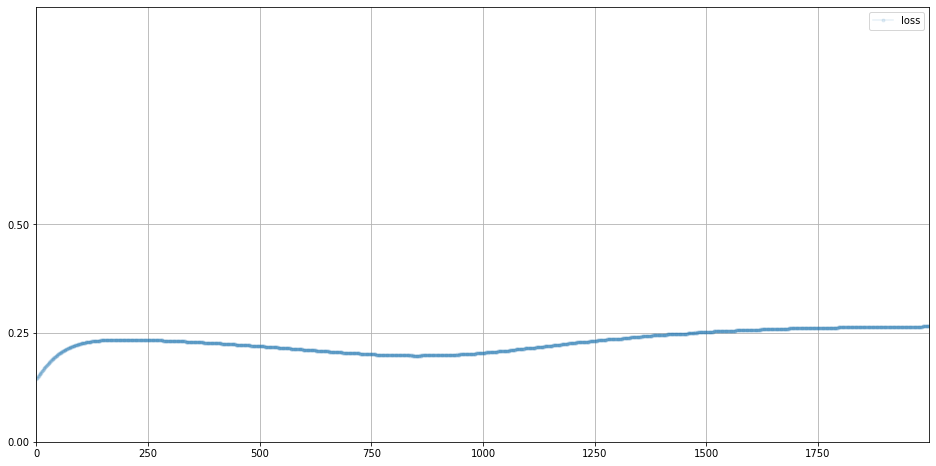
# plot discriminator error
D.plot_progress()
In [0]:
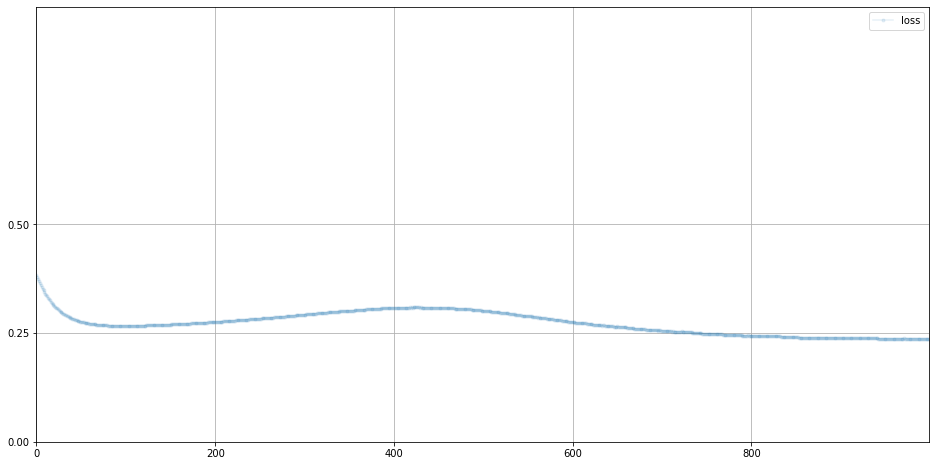
# plot generator error
G.plot_progress()
Manually Run Generator
In [0]:
# manually run generator to see it's outputs
G.forward(torch.FloatTensor([0.5]))
Out[0]:
tensor([0.9387, 0.0527, 0.9389, 0.0474], grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward>)Visualise Pattern During Training
In [0]:
# plot images collected during training
plt.figure(figsize = (16,8))
plt.imshow(numpy.array(image_list).T, interpolation='none', cmap='Blues')
Out[0]:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f6f317b26d8>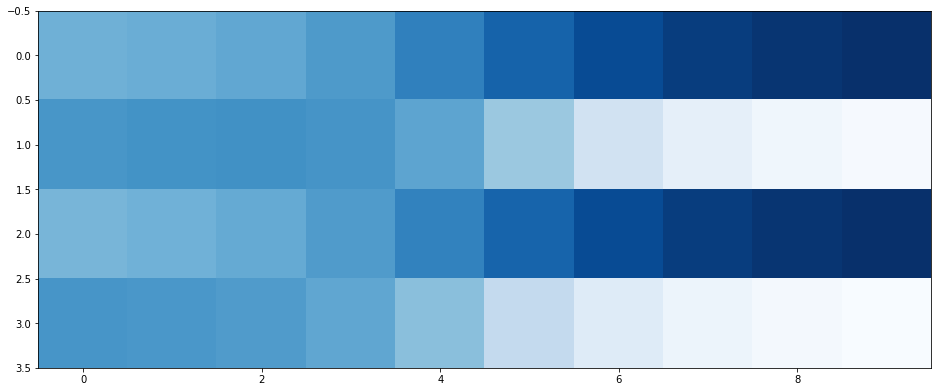
반응형
'인공지능' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 인스타 사진과 AI(인공지능)으로 3D모델 만들기 (0) | 2022.07.21 |
|---|---|
| Keras Model Compilation (0) | 2022.07.16 |
| KT AI Coding Pack (구 - AI Makers Kit) (0) | 2021.08.26 |
| 신경망 인공지능 vs 기호처리 인공지능 (0) | 2021.05.18 |
| 음성인식(Voice Recognition)과 인공지능 가상 비서(Artificial Intelligent Virtual Assistant) (0) | 2021.05.10 |



댓글